Non-transgenic GI-seeded beta-amyloid mouse model
Late-onset Alzheimer's diseases (AD) contributes to > 90% of AD patients compared to < 1 % of cases in familial AD. Significant amount of funding had been put on research using transgenic models based on beta-amyloid or tau hypothesis. However, in the past decade, all clinical trials based on these research had failed. The cause of late-onset AD is unknown but likely involves environmental factors, including diets, contaminants, stress and other living habits. We believe that a non-transgenic long-term research model is required to represent the > 90% late-onset AD populations for revolutionary research on early diagnostics and new therapeutic treatment strategies.
Our model based on the brain-gut axis and prion hypothesis
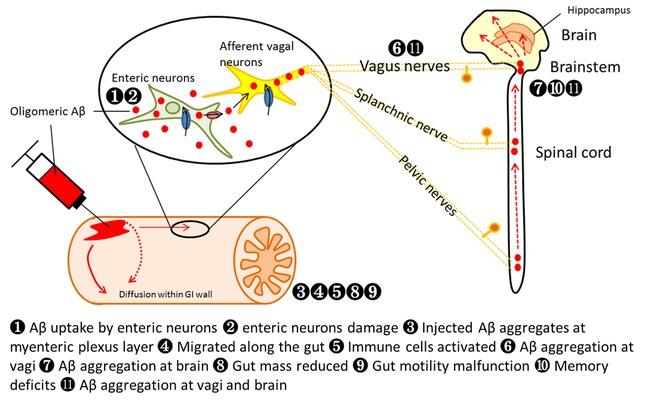
We recently published two leading articles using our newly-developed late-onset AD model of the mouse through injecting soluble oligomeric beta-amyloid (1-42) into the gastrointestinal (GI) wall in 2-month-old young mouse and seeded for a year. The model makes use of misfolded beta-amyloid in the gut to trigger cascades of misfolding of beta-amyloid, and hypothesize to be translocated from the gut to the brain via neuronal, immunological and vascular pathways similar to the prion protein.
Evidences we found:
|
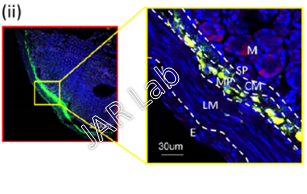
In 1 month tracking study,
After intra-GI injection of beta-amyloid in-vivo, fluorescently-labelled beta-amyloid:
|
|
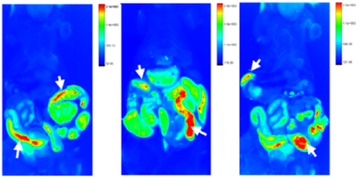
In 6 month long-term in-vivo model,
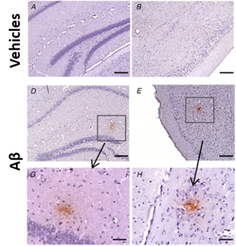
In 12 month long-term in-vivo model,
|
Summary
References
- Alzheimer’s_Association. Alzheimer’s Association 2020 Facts and Figures Report. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2020
- Liu YH, Sun YY, Sommerville N, Ngan MP, Ponomarev ED, Lin G & Rudd JA (2020). Soy flavonoids prevent cognitive deficits induced by intra-gastrointestinal administration of beta-amyloid. Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association, 141 111396.
- Sun YY, Sommerville NR, Liu YH, Ngan MP, Poon D, Ponomarev ED, Lu ZB, Kung JS & Rudd JA (2020). Intra-gastrointestinal amyloid-beta 1-42 oligomers perturb enteric function and induce Alzheimer's disease pathology, Journal of Physiology-london, 598(19), 4209-4223.