Gastrointestinal Pacemaker Activity
We recently introduce the microelectrode array (MEA) technique to record gastrointestinal (GI) pacemaker activity, or slow waves. Interstitial cell of Cajal (ICCs) is responsible for producing electrical rhythmic low-frequency waves called slow waves to control smooth muscle peristalsis in the GI tract. We aim to apply this technique in drug testing and screening to study the mechanism of gut dysrhythmia.
|
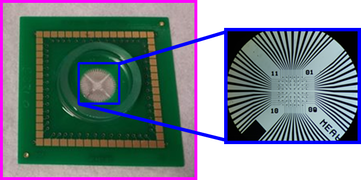
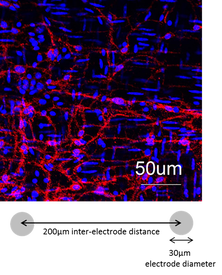
Our MEA chips for recording GI pacemaker potentials consist of 60-electrode with inter-electrode distance of 200 μm. Each electrode is 30 μm in diameter and 30 μm in height.
|
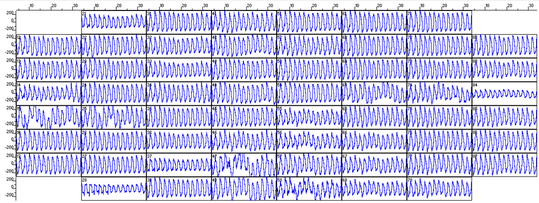
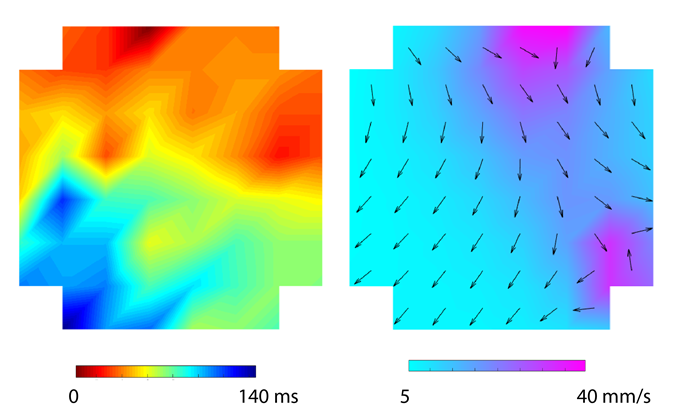
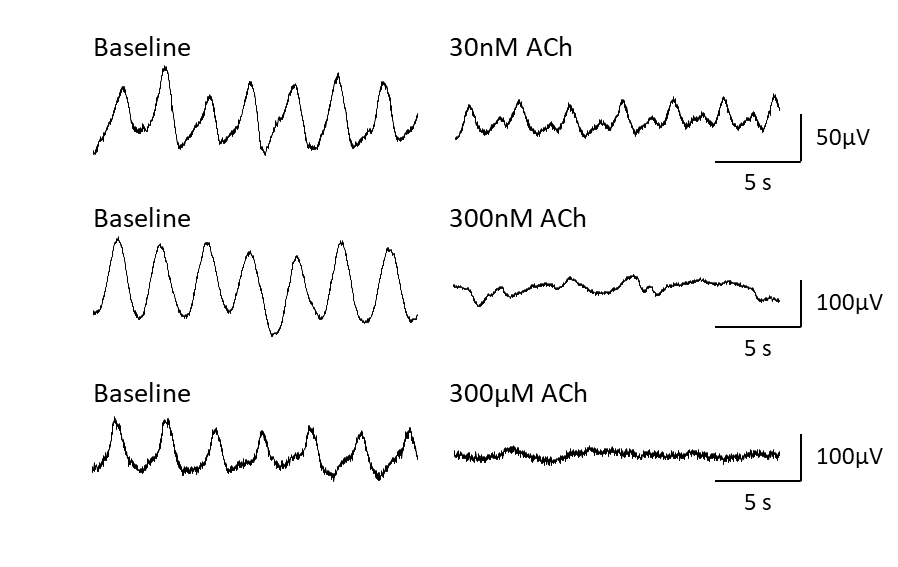
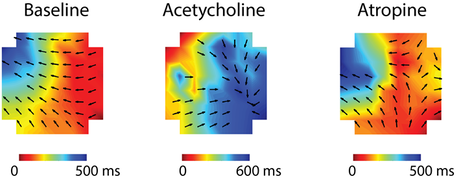
The 60-channel MEA system allows simultaneous recording from 60 electrodes. The picture above shows a caption of raw traces recorded from the duodenum of the mice.
|
|
Colon treated with cisplatin
|
Baseline recording of the duodenum in the Suncus murinus
|
References
- Liu YH, Du P & Rudd JA (2020). Acetylcholine Exerts Inhibitory and Excitatory Actions on Mouse Ileal Pacemaker Activity: The Role of Muscarinic versus Nicotinic Receptors. American journal of physiology. Gastrointestinal and liver physiology, 319(1), G97-G107.
- Liu YH, Du P, Chan WY & Rudd JA (2019). Use of a microelectrode array to record extracellular pacemaker potentials from the gastrointestinal tracts of the ICR mouse and house musk shrew (Suncus murinus). Cell Calcium, 80, 175-188.